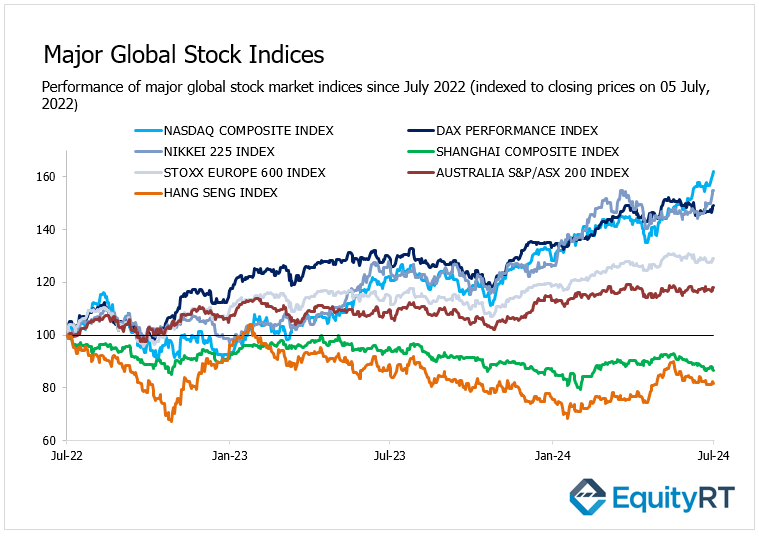
Global Markets Recap
Despite the slight rise in the unemployment rate and the slowdown in average hourly earnings, consistent with expectations indicating a cooling labor market, Wall Street indices closed higher. This was driven by growing expectations of interest rate cuts from the Fed this year.
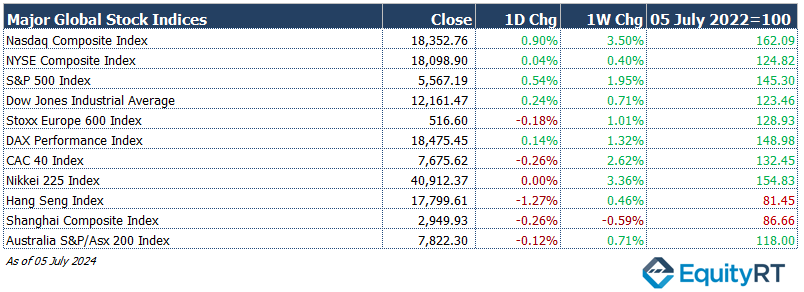
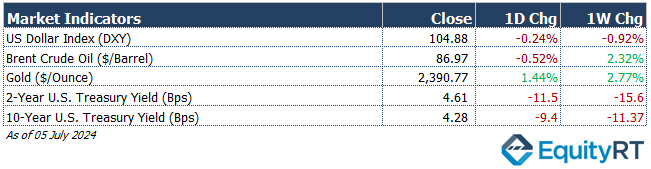
The Dollar Index (#DXY), a closely watched gauge of the U.S. dollar’s performance against other major currencies, closed last week at 104.88 marking a 0.92% weekly loss.
The Brent crude oil (#LCO07) closed the previous week at USD 86.97 per barrel, reflecting a 2.32% weekly gain.
The price of gold (#XAU) closed last week with a 2.77% gain, settling at USD 2,390.77 per ounce.
The 2-year U.S. Treasury yield (#USGG2YR), particularly responsive to Federal Reserve policy rates, closed at 4.61% with a 15.6 basis points weekly loss. The 10-year U.S. Treasury yield (#USGG10YR) completed the week with a 11.37 basis points loss, settling at 4.28%.
Take the Guesswork out of Investing: Backtest Your Strategies with Ease!
Key Economic Indicators Released Last Week in the US
Let’s take a look at the macroeconomic indicators and developments tracked in the US last week:
- U.S. Employment Market Data
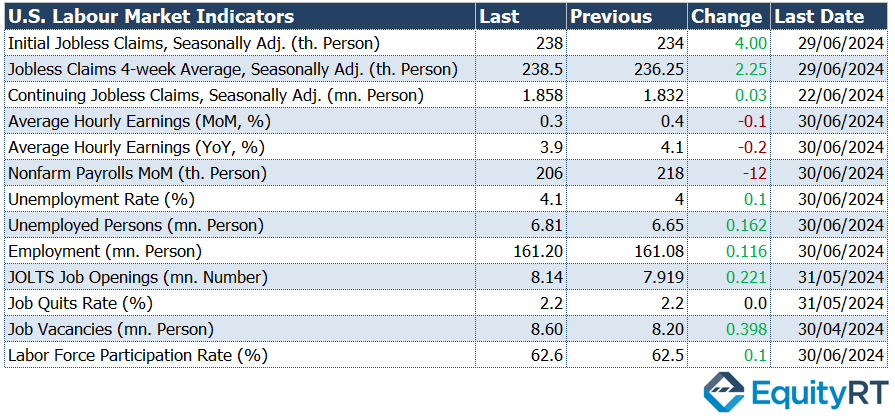
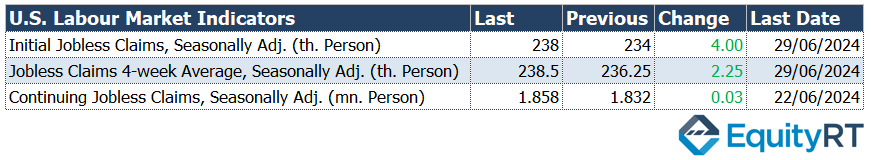
For the week ending June 29, weekly initial jobless claims rose from 234,000 to 238,000, exceeding expectations but still indicating a relatively tight labor market. The claims remained at historically low levels.
In June, non-farm employment growth slowed from 218,000 to 206,000, still above expectations of 190,000. The May data was revised down significantly from 272,000 to 218,000, a reduction of 54,000, and the April data was revised down by 57,000 to 108,000. Thus, the total employment growth for the previous two months was revised down by 111,000.
The unemployment rate rose slightly from 4% to 4.1% in June, the highest since November 2021. Expectations were for the rate to remain steady at 4%.
The number of unemployed increased by 162,000 to 6.81 million, while the number of employed rose by 116,000 to 161.2 million.
The growth rate of average hourly earnings, a key indicator for inflation, slowed in June from 0.4% to 0.3% monthly, aligning with expectations. Annually, the growth rate decreased from 4.1% to 3.9%, the lowest since June 2021.
Given these factors, investors’ expectations for two interest rate cuts from the Fed this year have increased.
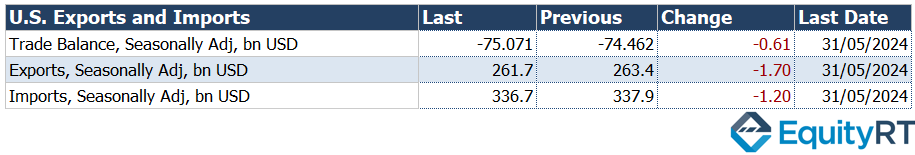
- U.S. Trade Balance for May
The U.S. trade balance data for May showed that the monthly trade deficit increased from $74.5 billion to $75.1 billion, the highest since October 2022 but below expectations. Monthly imports fell by 0.4% to $336.7 billion, while exports decreased by 0.7% to $261.7 billion.
Unleash Your Investment Potential. EquityRT might be the missing puzzle piece to reach your ultimate investment strategy.
Key U.S. Economic Indicators to Watch This Week
In the U.S., the market’s focus will be on Fed Chair Powell’s speeches on Tuesday and Wednesday. Investors will be looking for new clues about the Fed’s future monetary policy and potential interest rate cuts.
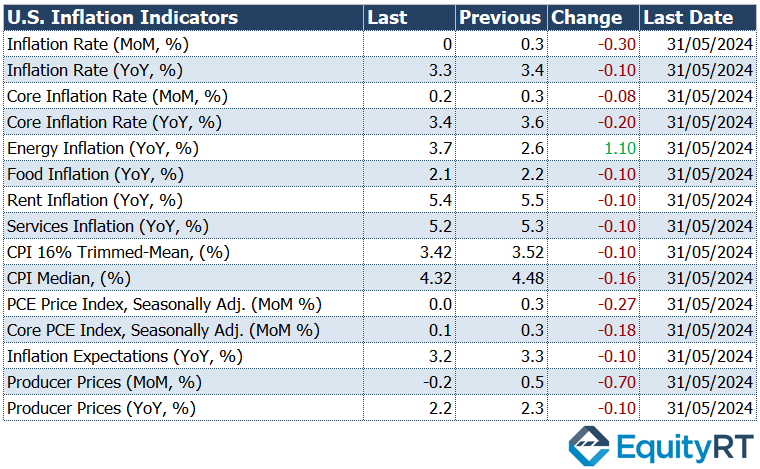
Additionally, important data closely watched for Fed’s monetary policy guidance will be released this week. On Thursday, June’s CPI data will be released, followed by June’s PPI data on Friday
In May, the headline CPI monthly growth rate slowed from 0.3% to 0%, marking the lowest level since July 2022, and came in below expectations (0.1%). Annually, it fell from 3.4% to 3.3%, also below expectations (3.4%).
Excluding food and energy prices, the core CPI monthly growth rate slowed from 0.3% to 0.2%, below expectations (0.3%), marking the lowest level in seven months. Annually, it slowed from 3.6% to 3.4%, the lowest since April 2021.
Excluding food and energy products, the core PPI remained flat in May after a 0.5% increase in April, below expectations of a 0.3% increase. Annually, it fell from 2.5% to 2.3%.
For June, the headline CPI is expected to accelerate from 0% to 0.1% monthly and decrease from 3.3% to 3.1% annually. The core CPI is expected to maintain a similar monthly growth rate of 0.2% and an annual rate of 3.4%.
In May, the headline PPI recorded a 0.2% decline following a 0.5% increase in April, marking the sharpest drop since October. Expectations were for a modest 0.1% increase. Annually, it fell slightly from 2.3% to 2.2%, below expectations of a rise to 2.5%.
For the headline PPI, a 0.1% monthly increase is expected in June after a 0.2% decline in May, with an annual rise from 2.2% to 2.3%. The core PPI is expected to accelerate from 0% to 0.2% monthly and rise from 2.3% to 2.5% annually.
- Employment Market Data
On Thursday, the weekly initial jobless claims data will be monitored. The last reported initial jobless claims rose from 234,000 to 238,000, exceeding expectations but still indicating a relatively tight labor market and remaining at historically low levels.
- Consumer Sentiment Index
On Friday, the preliminary data for the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index for July will be followed. The final index for June was revised up slightly from 65.6 to 68.2, surpassing expectations (66).
Take the guesswork out of investing: Backtest your strategies with ease!
Key Economic Indicators From Europe Last Week
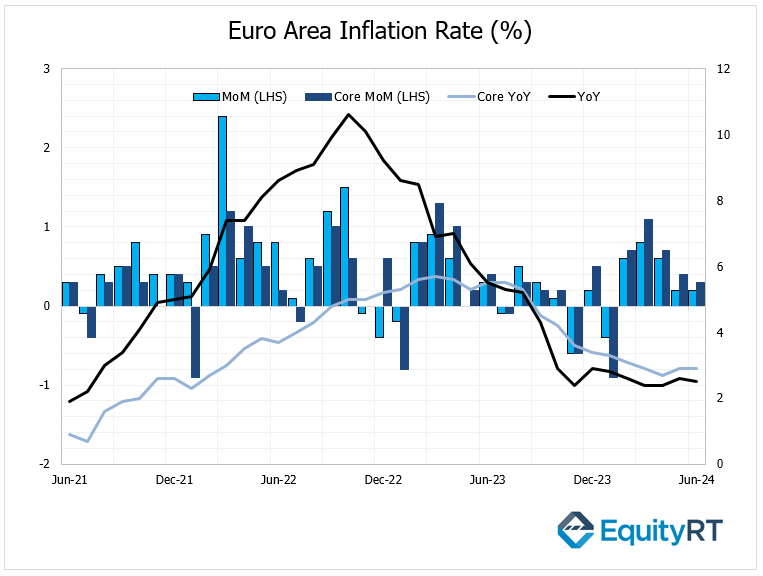
The preliminary CPI data for June was released. The headline CPI in the Euro Area recorded a monthly growth rate of 0.2% in June, similar to the previous month and in line with expectations, marking the lowest level in five months. Annually, it slightly decreased from 2.6% to 2.5%, indicating gradual progress towards the ECB’s 2% target. Core CPI remained steady at 2.9% annually in June, similar to the previous month, while expectations were for a slight decrease to 2.8%.
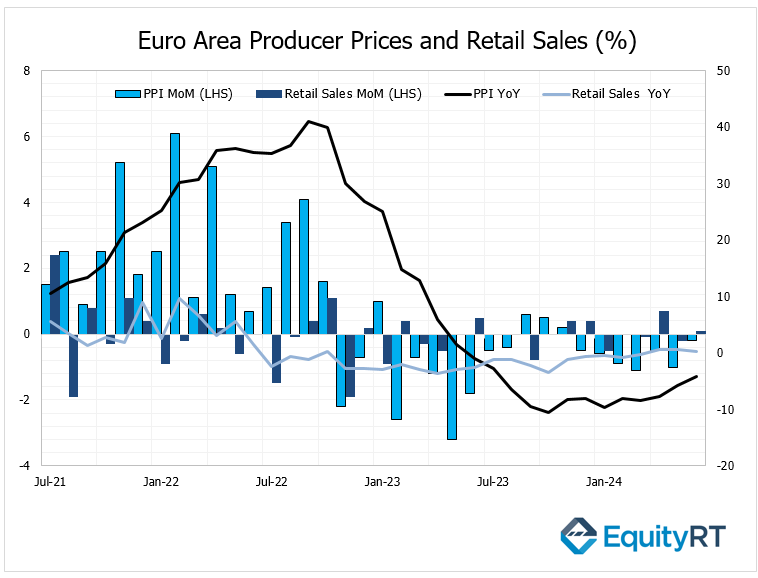
- Euro Area Producer Price Index (PPI) and Retail Sales
The Euro Area’s PPI decreased by 0.2% in May following a 1% drop in April, continuing its decline for the seventh consecutive month. Annually, the decline slowed from 5.7% to 4.2%, maintaining its downward trend for thirteen months.
Retail sales data for May in the Euro Area, an indicator of domestic demand, showed a partial recovery with a 0.1% monthly increase following a 0.2% decrease in April. Annually, the growth rate slowed from 0.6% in April to 0.3% in May.
- Germany’s Industrial Production and Factory Orders
Germany’s industrial production data for May was released, showing a 2.5% monthly decline following a modest 0.1% increase in April. This decline was the sharpest since late 2022. Annually, the contraction in industrial production accelerated from 3.7% to 6.7%, the fastest decline since August 2020.
Factory orders in Germany fell by 1.6% in May due to weak external demand, following a 0.6% decrease in April. This marked the sharpest decline since January and extended the series of monthly declines to five.
Unleash Your Investment Potential. EquityRT might be the missing puzzle piece to reach your ultimate investment strategy.
European Economic Trends: This Week’s Market Insights
- German Inflation Data
On Thursday, the final CPI data for June, which will guide the ECB’s monetary policy, will be released. In Germany, the monthly growth rate of the headline CPI in June was 0.1%, similar to the previous month, marking the lowest level in six months and falling short of expectations (0.2%). Annually, it slightly decreased from 2.4% to 2.2%, whereas expectations were for a decline to 2.3%. Additionally, the annual core CPI in Germany fell from 3% to 2.9% in June, the lowest level since February 2022.
- UK GDP Data
On Thursday, the UK’s GDP growth data for May will be tracked. Following three months of growth (0.3% in January, 0.2% in February, and 0.4% in March), the UK economy remained stagnant in April (0%), contrary to expectations of a 0.1% contraction.
Take the guesswork out of investing: Backtest your strategies with ease!
Asian Economic Indicators
In June 2024, South Korea’s trade surplus grew to USD 8.92 billion from USD 1.26 billion last year, surpassing expectations. Exports rose by 11.1% to USD 58.95 billion, and imports fell by 1.9% to USD 50.20 billion.
Japan’s consumer confidence index rose slightly to 36.4 in June, below the expected 36.5.
Japan’s foreign exchange reserves fell slightly to USD 1.231 trillion in June, the lowest since February last year, due to government intervention.
Upcoming Asian Data
China’s June foreign trade data, expected on Friday, predicts an 8% annual increase in exports and a 2.5% annual rise in imports.
This week on Tuesday, Taiwan will release its foreign trade data, and China will report its vehicle sales. Wednesday will see China’s inflations, along with South Korea’s unemployment rate and Japan’s producer prices.
On Thursday, China will release its GDP, New Yuan Loans and M2 Money Supply. Friday will bring China’s foreign trade data.
Additionally, central bank meetings to watch include the Reserve Bank of New Zealand on Wednesday and the Bank of Korea on Thursday, with both banks expected to keep their policy rates unchanged.
