Global Markets Recap
U.S. Markets:
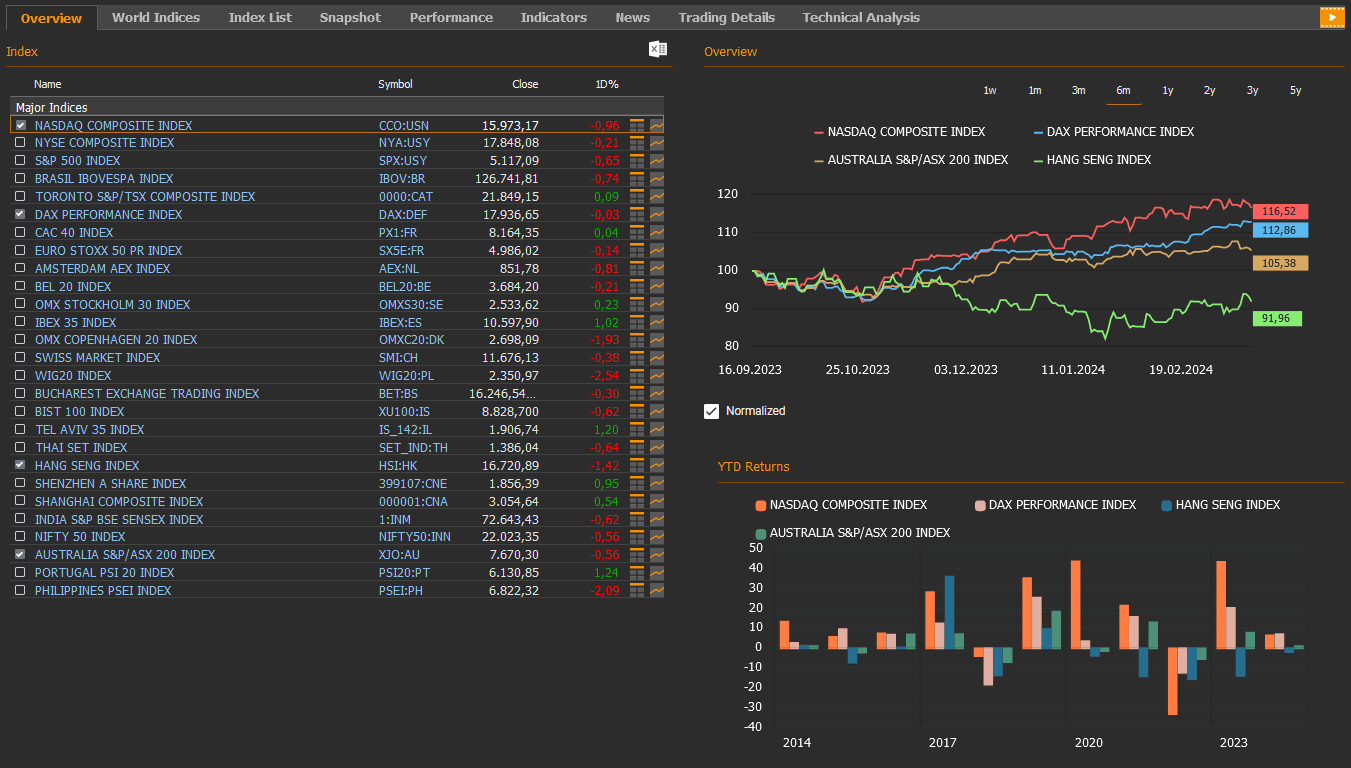
- On Friday, there was a decline in U.S. stocks, primarily driven by technology-related megacaps. On a daily basis, the Nasdaq composite index (CCO:USN) fell by 0.96% to 15,973.17, the NYSE composite index (NYA:USY) decreased by 0.21% to 17,848.08, the S&P 500 index (SPX:USY) dropped by 0.65% to close at 5,117.09, and the Dow Jones Industrial Average index (DJI:DJ) declined by 0.49% to 38,714.77.
- The Dollar Index (DXY), a closely watched gauge of the U.S. dollar’s performance against other major currencies, closed last week at 103.4 marking a 0.7% weekly increase.
- The Brent crude oil (LCO07:USC) closed the previous week at USD 85.3 per barrel, reflecting a weekly 4% rise.
- The price of gold (XAU/USD:USC) closed last week with a 1% drop, settling at USD 2,155,5 per ounce.
- The 10-year U.S. Treasury yield (USGG10YR:BND) completed the week with a 22 basis points increase, settling at 4.31%. The 2-year U.S. Treasury yield (USGG2YR:BND), particularly responsive to Federal Reserve policy rates, finished at 4.73% up by 25 basis points.
European Markets:
- European stocks finished mostly down Friday, as the Stoxx Europe 600 index (SXXP:FR) lost 0.32% to 504.80. The German DAX index (DAX:DEF) decreased 0.03% to 17,936.65, and the French CAC 40 index(PX1:FR) added 0.04% to 8,164.35.
Asian Markets:
- Stocks in the Asia-Pacific region mostly down on Friday, March 15. Hong Kong stocks decreased with the Hang Seng index (HSI:HK) lost 1.42% at 16,720.89, while the Nikkei 225 index (100000018:JPT) down by 0.26% to 38,707.64 and China’s Shanghai Composite index (000001:CNA) rose 0.54% to 3,054.64.
- The S&P/ASX 200 Benchmark index (XJO:AU) in the Australian stock market lost 0.56% to 7,670.30.
Take the Guesswork out of Investing: Backtest Your Strategies with Ease!
Overview of Key Economic Indicators in the US Last Week
Let’s take a look at the macroeconomic indicators and developments tracked in the US last week:
- Inflation Expectations
According to the Consumer Expectations Survey for February released by the New York Fed, the consumer inflation expectations for the year ahead remained unchanged at 3% in February, maintaining its lowest level since January 2021. While the inflation expectations for the next three years rose slightly from 2.4% to 2.7%, the long-term expectation covering five years increased slightly from 2.5% to 2.9%.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI)
In February, the headline Consumer Price Index (CPI) in the US increased from 0.3% to 0.4% on a monthly basis, recording the strongest increase in the past five months. On an annual basis, it rose slightly from 3.1% to 3.2%. The increase in the CPI was driven by renewed increases in energy products, used vehicle, and apparel prices, along with the service prices maintaining their high levels despite a partial slowdown. However, stable food prices and a slight decrease in new vehicle prices limited the monthly CPI increase.
The core CPI, which excludes food and energy prices, increased by 0.4% on a monthly basis in February, exceeding expectations (0.3%) and reaching its highest level in the past ten months. On an annual basis, it decreased slightly from 3.9% to 3.8%, marking the lowest level in approximately the past three years.
- Producer Price Index (PPI)
The headline Producer Price Index (PPI) in the US recorded a strong increase of 0.6% on a monthly basis in February, surpassing expectations (0.3%) and marking the strongest increase in the past six months.
Goods prices increased by 1.2%, marking the largest rise in six months. This was mainly driven by a 4.4% surge in energy costs and a 1.0% uptick in food prices. The core producer inflation rate, which excludes more volatile items such as food and energy, went up by 0.3%. This indicates a slowdown from the 0.5% increase seen in January but is slightly higher than the expected 0.2%.
On an annual basis, the producer prices in the US rose from 1% to 1.6% exceed expectations (1.1%), reaching its highest level in the past five months.
- Retail Sales and Labor Market
Retail sales in the US showed a partial recovery in February, increasing by 0.6% after a 1.1% decline in January, but falling short of expectations (0.8%). However, core retail sales, excluding automobiles, gasoline, food, and building materials, remained stagnant in February after a 0.3% decline in January. These data indicate that consumer spending and domestic demand recorded partial recoveries below expectations.
Data from the US labor market showed that weekly initial jobless claims for the week ending March 9, despite expectations of a slight increase, fell to 209,000 from 210,000, reaching their lowest level in the past three weeks and remaining below historical averages, indicating continued tightness in the labor market.
Meanwhile, the number of people receiving unemployment benefits for consecutive weeks increased by 17,000 to 1,811,000 in the last week, which was lower than the market’s expectation of 1,900,000. The four-week moving average stood at 208,000, down by 500 from the revised average of the previous week. The average of the previous week was adjusted downward by 3,750, from 212,250 to 208,500.
- The University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment
In March 2024, the University of Michigan consumer sentiment for the US declined to 76.5, marking its lowest level in three months, down from 76.9 in February, and falling below forecasts of 76.9. Preliminary estimates revealed that minor improvements in personal finances were counterbalanced by slight decreases in expectations for business conditions.
- Capacity Utilization Rate
The capacity utilization rate in the US remained stable at 78.3% in February, unchanged from a downwardly revised 78.3% in January, which was below market expectations of 78.5%. This rate now sits 1.3 percentage points below its long-term average. However, capacity utilization for manufacturing increased by 0.6 percentage points to 77%, still 1.2 percentage points below its long-term average.
- Industrial and Manufacturing Production
Industrial production in the US rose by 0.1% from the previous month in February 2024, indicating a recovery from two consecutive months of decline. This performance was contrary to market expectations of no growth.
Notably, manufacturing output, comprising 78% of total production, experienced a robust increase of 0.8%, bouncing back from a downwardly revised 1.1% drop in January. Additionally, mining output improved by 2.2%, partially due to recovery from weather-related setbacks in January. Durable manufacturing registered a gain of 1%, while nondurable output increased by 0.7%. However, the output of other manufacturing sectors, such as publishing and logging, saw a slight decrease of 0.1%.
- Export and Import Prices
In February 2024, export prices in the US rose by 0.8% month-over-month, following a 0.9% advance in January, surpassing market expectations of a 0.2% increase. On the other hand, US import prices increased by 0.3% from the previous month in February 2024, matching market expectations. However, import prices fell by 0.8% year-on-year, marking the 13th consecutive month of decline. Nonetheless, this decline represented the slowest pace since February 2023.
Unleash Your Investment Potential. EquityRT might be the missing puzzle piece to reach your ultimate investment strategy.
U.S. Economic Data Highlights for the Week
This week in the United States, all eyes will be on Wednesday’s Federal Reserve (Fed) interest rate decision and Fed Chair Powell’s speech. Additionally, the Fed’s new interest rate path and macroeconomic projections will be released.
During its January meeting, the Fed opted to keep the federal funds rate range steady at 5.25% to 5.50%, meeting market expectations. This marked the fourth consecutive meeting without any changes in interest rates, and the decision was reached unanimously. Furthermore, the Fed hinted at the possibility of rate cuts but emphasized that any adjustments would not occur immediately. It’s anticipated that there won’t be any rate cuts in Wednesday’s meeting.
Thursday will bring attention to the Global Manufacturing and Services Sector Flash Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) data for March, along with the weekly initial jobless claims data from the labor market.
In February, the revised manufacturing sector PMI data, up from 51.5 to 52.2, indicated a slight uptick in growth, hitting its highest level since July 2022 and extending its expansionary trend into the second consecutive month. Similarly, the revised service sector PMI data for February, up from 51.3 to 52.3, signaled a modest acceleration in growth, maintaining its expansionary trajectory for the past 13 months.
The recently released weekly initial jobless claims, despite expectations of a slight increase, declined from 210,000 to 209,000, reaching the lowest level in the past three weeks, and remained below historical averages, indicating a tight labor market condition.
Housing market data will also be closely monitored, with February housing starts and building permits scheduled for release on Tuesday, and existing home sales data on Thursday.
Take the guesswork out of investing: Backtest your strategies with ease!
European Economic Outlook and Economic Events
Based on the inflation numbers that influence the ECB’s money decisions, the final Consumer Price Index (CPI) for February in Germany went up by 0.4% compared to the previous month, which matches the earlier estimates. This increase follows a 0.2% rise in January. Looking at the year-on-year basis, CPI in Germany dropped from 2.9% to 2.5%, marking its lowest level since June 2021. Similarly, the annual core CPI in February stayed steady at 3.4%, hitting its lowest point since June 2022.
In the Eurozone, industrial production saw a significant drop of 3.2% in January after going up by 1.6% in December compared to the previous month. This decline indicates the most severe contraction since March of the previous year. Year-on-year, industrial production in January experienced a 6.7% decrease after a slight 0.2% growth in December, marking the sharpest decline in the last four months.
At the same time, wholesale prices in Germany continued their downward trend in February 2024, showing a 3% decrease compared to the previous year, continuing from the 2.7% decline in the previous month. On a monthly basis, wholesale prices went down by 0.1% in February after a 0.1% increase in the previous month.
In the UK, the monthly Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth data for January was released, showing a 0.2% growth in January, as expected, following a 0.1% contraction in December.
In February 2024, France’s annual inflation rate decreased slightly to 3% from 3.1% in the previous month, higher than the preliminary estimates of 2.9%. This marks the lowest figure observed since January 2022.
Unleash Your Investment Potential. EquityRT might be the missing puzzle piece to reach your ultimate investment strategy.
Economic Indicators in Focus This Week in the European Region
- Eurozone CPI, Trade Balance, and German Economic Sentiment
On Monday, final CPI data for February and trade balance data for January were released in the Eurozone.
In February 2024, the Euro Area’s consumer price inflation stayed at 2.6% compared to the previous year, marking a three-month low but still above the European Central Bank’s 2% target. Energy prices fell by 3.7% compared to -6.1% in January, while price increases for food, alcohol & tobacco slowed to 3.9% (from 5.6%, and non-energy industrial goods rose by 1.6% down from 2.0%. However, services inflation remained stable at 4.0%. Excluding volatile food and energy prices, the core inflation rate was also steady at 3.1%, its lowest since March 2022.
In January 2024, the Eurozone recorded a trade surplus of €11.4 billion, a significant turnaround from the €32.6 billion deficit reported in the same month last year.
In Germany, the ZEW Economic Sentiment Index for March will be released on Tuesday. In February, despite expectations for a slight recovery, the ZEW Current Conditions Index fell from -77.3 to -81.7, surpassing expectations (-81.5) and hitting its lowest level since June 2020, maintaining its weak trend in the negative territory.
- ECB President Lagarde’s Speech
On Wednesday, ECB President Lagarde’s speech will be the focal point in European markets. Clues she might provide regarding monetary policy and the timing of potential interest rate cuts will be closely monitored.
- Germany’s PPI, UK’s CPI, and Eurozone’s Consumer Confidence
On Wednesday, new economic data will be released, including the Producer Price Index (PPI) for February in Germany, the Consumer Confidence Index flash data for March in the Eurozone, and the Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for February in the UK.
In Germany, the PPI increased by 0.2% in January after declining by 1.2% in December, marking an end to its three-month streak of decline. However, the year-on-year decrease slowed down from 5.1% to 4.4% in January. For February, it is expected that the PPI will decrease by 0.2% monthly, with the annual decrease slowing down to 3.8% from 4.4%.
The Consumer Confidence Index in the Eurozone slightly improved from -16.1 to -15.5 in February, although it remained in negative territory. It is anticipated to continue improving to -14.7 in March.
In the UK, after a 0.4% increase in headline CPI in December followed by a 0.6% decrease in January, expectations are for a 0.3% decrease. The annual CPI remained at 4%, while expectations were for a slight increase to 4.1%. Core CPI in the UK experienced its largest decline in a year, with a 0.9% decrease in January following a 0.6% increase in December.
For February, a 0.7% increase in headline CPI is expected, along with a decrease in annual CPI to 3.6% from 4%, and the annual core CPI is expected to decrease from 5.1% to 4.6%.
- Preliminary HCOB Manufacturing and Services PMI Data for Eurozone
In Europe, the flash HCOB Manufacturing and Services PMI figures for March will be published on Thursday. Last February, manufacturing PMIs stayed below the 50 mark indicating contraction, mainly because of tighter finances and weaker demand. Service PMIs also stayed in contraction territory below the 50 mark in February, except for the UK and the Eurozone.
- Central Bank Meetings
On Thursday, the Bank of England (BoE) will hold its meeting. During its February meeting, the BoE decided to keep its policy rate steady at 5.25%, as anticipated, maintaining it at the highest level seen in 15 years. It is anticipated that the BoE will maintain this policy rate during this week’s meeting.
Additionally, on the same day, the meetings of the Swiss National Bank and the Norges Bank will be closely monitored. The Swiss National Bank is expected to keep its policy rate unchanged at 1.75%, while the Norges Bank is anticipated to maintain its policy rate at 4.50%.
- IFO Business Climate Index for Germany
On Friday, Germany’s IFO Business Climate Index data for March will be released. In February, the IFO Business Climate Index slightly rose from 85.2 to 85.5, the lowest level since October 2022, in line with expectations. The index is expected to slightly increase to from 85.5 to 85.9.
Take the guesswork out of investing: Backtest your strategies with ease!
Economic Indicators in Asia for the Week
China’s urban unemployment rate rose to 5.3% in January-February 2024, up from 5.1% in December, marking its highest level since July. The rate for local registered labor stood at 5.5%, while that for migrant workers was at 4.8%.
In the same period, China’s industrial production surged by 7.0% year-on-year, outpacing December’s 6.8% growth and exceeding market expectations of 5%. This expansion represented the fastest growth in industrial output in nearly two years.
Additionally, China’s fixed-asset investment grew by 4.2% year-on-year in January-February 2024, surpassing market forecasts of 3.2%.
On the retail front, China’s retail sales increased by 5.5% year-on-year in January-February 2024, exceeding the market consensus of 5.2%. This growth marked the 13th consecutive month of expansion in retail trade.
Meanwhile, Japan’s core machinery orders declined by 1.7% month-on-month to 823.8 billion yen in January 2024, reversing from a 1.9% gain in December and falling below market expectations of a 1% drop.
Investors will also keep an eye on other economic indicators, including Japan’s BOJ interest rate decision, China’s industrial profits and loan prime rates for 1 year and 5 years, Indonesia’s interest rate decision, Russia’s interest rate decision and manufacturing and services PMIs for India.
