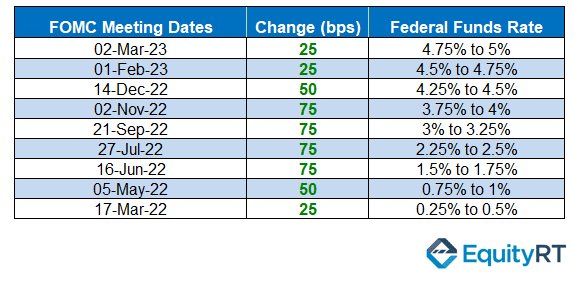
The KBW Banking Index is the reference stock index for the banking sector. In February 2023, the KBW Bank Index recorded a drop of more than 15% y/y, with Bank of America (NYSE: BAC) and JPMorgan Chase (NYSE: JPM), the biggest names in the market, leading the losses in the index. The main factor in the bank’s value loss was the Federal Reserve’s decision to raise interest rates by a total of 475 basis points until its March 2023 meeting.
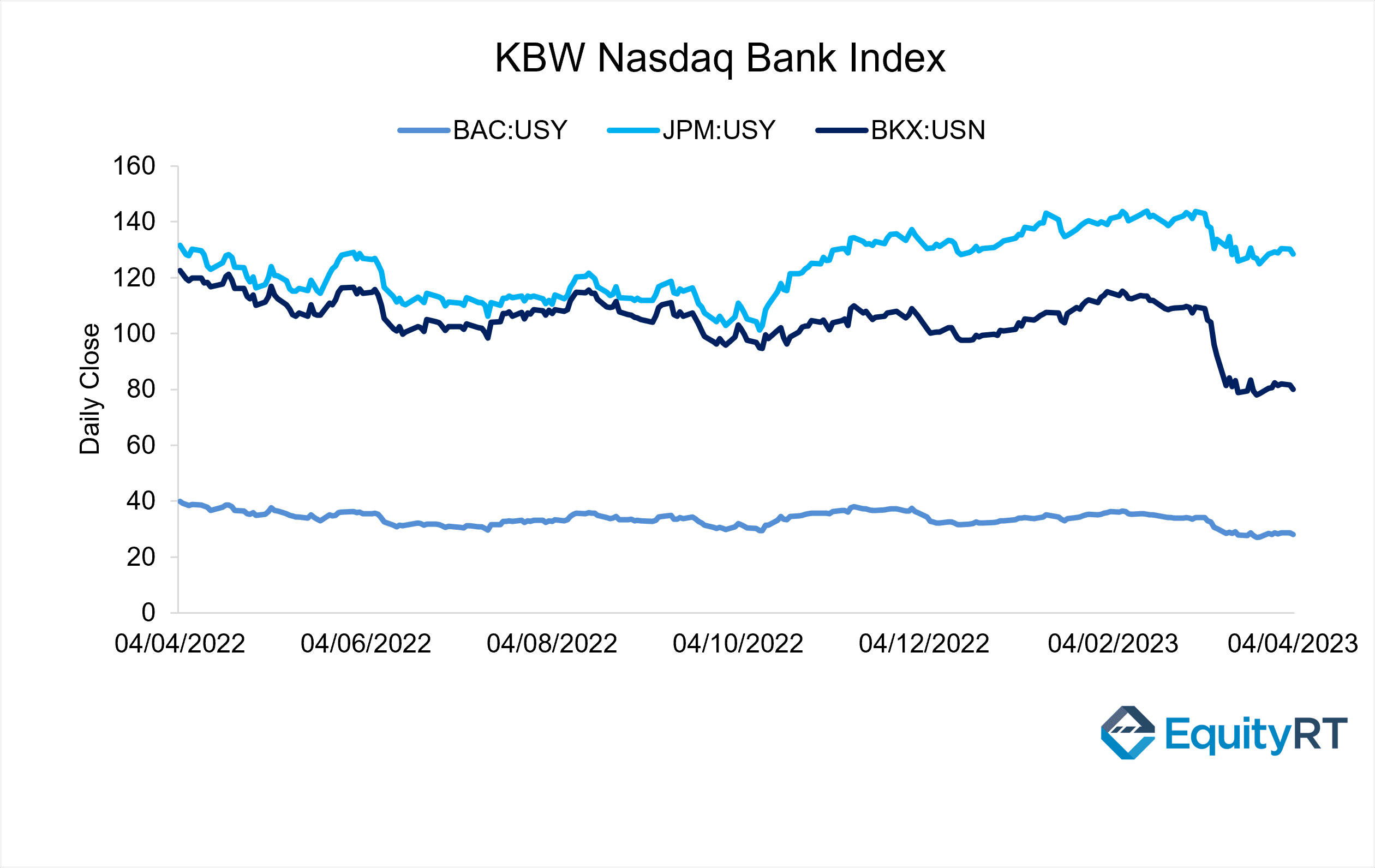
As a result, some banks in the US began to go bankrupt, and Silicon Valley Bank (SVB), one of the high-volume banks, went bankrupt on March 9th, triggering the banking crisis..
How did interest rate hikes trigger the crisis?
Unleash Your Investment Potential. EquityRT might be the missing puzzle piece to reach your ultimate investment strategy.
Why did Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) Collapse?
On March 8th, SVB Investment Bank, which is ranked 16th among the largest banks in the United States, has announced that it had recorded a post-tax loss of $1.8 billion due to the sale of its investments and plans to secure $2.25 billion in equity capital. The decision to recognize the losses on its available-for-sale securities was made to meet the withdrawal requests from customers. The news came as a surprise to investors and depositors who were previously unaware of any liquidity issues at SVB, despite them being evident on the bank’s balance sheet.
Large group of depositors triggered the crisis by quickly withdrawing their money from the bank. The bank’s share value continued to plummet, and on March 9th, it was declared bankrupt with a daily loss of 60%.
As a result, SVB has now become one of the largest bank bankruptcies since the financial crisis of 2008.
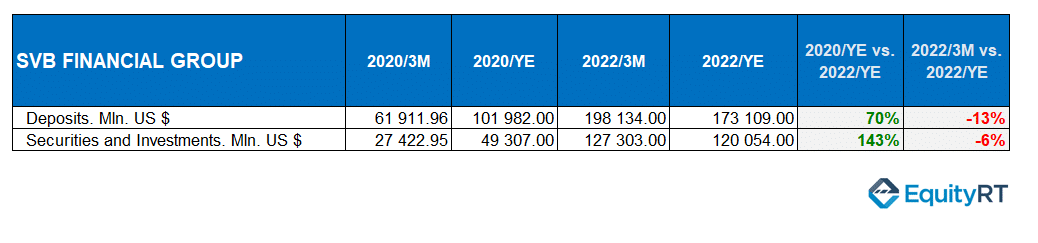
SVB has been funding a large number of technology companies, which have been performing well during the pandemic and keeping their profits in SVB as deposits. As a result, SVB’s deposits increased from approximately $62 billion in the first quarter of 2020 to $173 billion by the end of the fourth quarter of 2022.
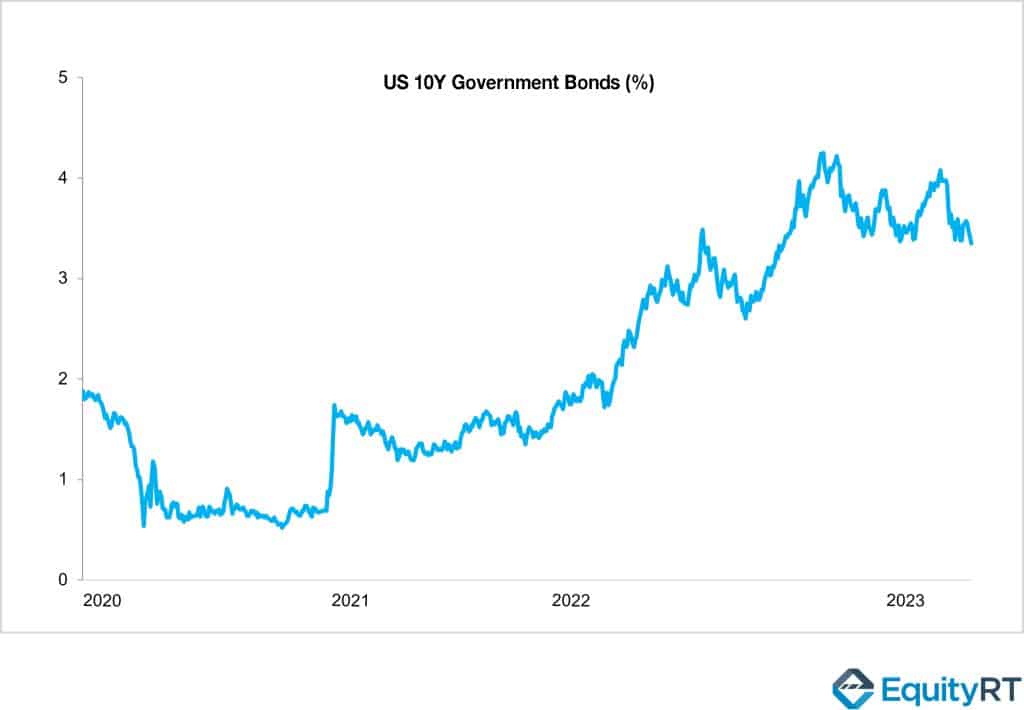
While SVB used some of these deposits for lending, the rest was invested in US Treasury securities with zero default risk. Therefore, SVB’s Treasury portfolio grew from $27 billion at the end of 2020 to $127 billion in the first quarter of 2022. However, when the Fed started raising interest rates and continued to do so sharply in the first quarter of 2022, this became a significant risk to SVB’s balance sheet, which held a large amount of government bonds.
By March 2022, the Fed had raised its interest rate to the highest level in history, ranging from 4.75% to 5%. As a result, SVB, which had a low-interest-rate securities inventory, experienced a decrease in the market value of its papers due to the Fed’s interest rate hikes
Signature Bank and Silvergate Capital Bank have both filed for bankruptcy.
Silvergate Capital, which specializes in cryptocurrency transactions, was the first bank to initiate the bankruptcy process. The bank had invested heavily in the cryptocurrency market through the FTX original cryptocurrency exchange and risk fund companies, as well as in treasury bonds. However, due to tight monetary policies and a decrease in high-interest treasury bonds, Silvergate suffered losses and filed for bankruptcy in November 2022 after the collapse of FTX. Similarly, Signature Bank had also invested a significant portion of its assets in the cryptocurrency market, leading to both banks’ bankruptcy.
Is the banking crisis in the US spreading contagiously?
Does the current banking crisis that originated in the US evoke memories of the 2008 crisis? While the 2008 crisis was caused by different reasons and affected the entire mortgage market, both crises have a common feature: their contagious nature. This is because, just as US banks experienced bankruptcies, banks in Europe, such as Credit Suisse, have also been flagged as potentially facing bankruptcies. The Swiss-based Credit Suisse Bank collapsed on March 15, and it was rescued by the Swiss National Bank via aid transfers.
Unleash Your Investment Potential. EquityRT might be the missing puzzle piece to reach your ultimate investment strategy.
Why did Credit Suisse face bankruptcy?
Although Credit Suisse experienced losses from interest income due to the rapid pace of interest rate increases, it was primarily impacted by the collapse of other banks. As a result, Credit Suisse’s story took on a different form.
Similar to the 2008 crisis, a period of rapid bank withdrawals started. The essence of a bank’s business is to borrow money, but there is always a risk of default on the bank’s debt. Lenders seeking protection against such risks purchase credit default swaps to cover against default, similar to obtaining car insurance.
When a bank defaults, credit default swaps cover the losses for the lenders who purchased them. If a bank’s credit default swap values increase, it implies that more investors are rushing to purchase insurance. In other words, rising concerns resulted in more credit default swaps being taken out on Credit Suisse, which led to insurers demanding more money from the bank. This occurred because they started to believe that the probability of default was greater. This increased the bank’s credit margin, which raised the bank’s cost of capital. As a result, the high credit margin made it challenging for the bank to refinance its debt. In 2020/YE, when the Swiss National Bank (SNB) policy rate was -0.75%, Credit Suisse’s adjusted net interest income was approximately $10,7 billion.
In 2022, when the SNB raised interest rates to the 1% range, Credit Suisse’s adjusted net interest income dropped to $4.9 billion with the losses earnings from treasury bonds.
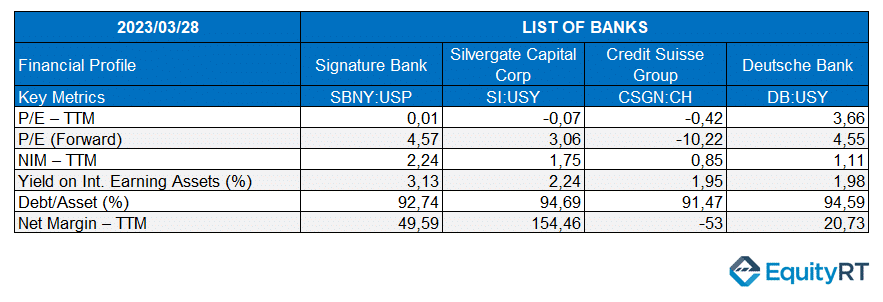
Deutsche Bank was not immune to the investor panic that resulted from the increasing risks in the banking sector. The bank’s credit default swaps (CDSs) also rose, indicating the rapid outflow of capital. The rising cost of insuring against defaults reflected the widespread fear that was spreading throughout the sector.
Consequently, on March 24th, Deutsche Bank, Germany’s largest lender, experienced a drop of up to 14% in its intraday stock values.
Deposits fled to gold and currency
As banks around the world were facing bankruptcy and their stock values were plummeting, deposit outflows from other countries, especially in the US, were significant.
During times of market volatility, investors tend to seek refuge in safe-haven assets such as gold and currency. The demand for gold has increased significantly due to the banking crisis, leading to a rise in gold prices
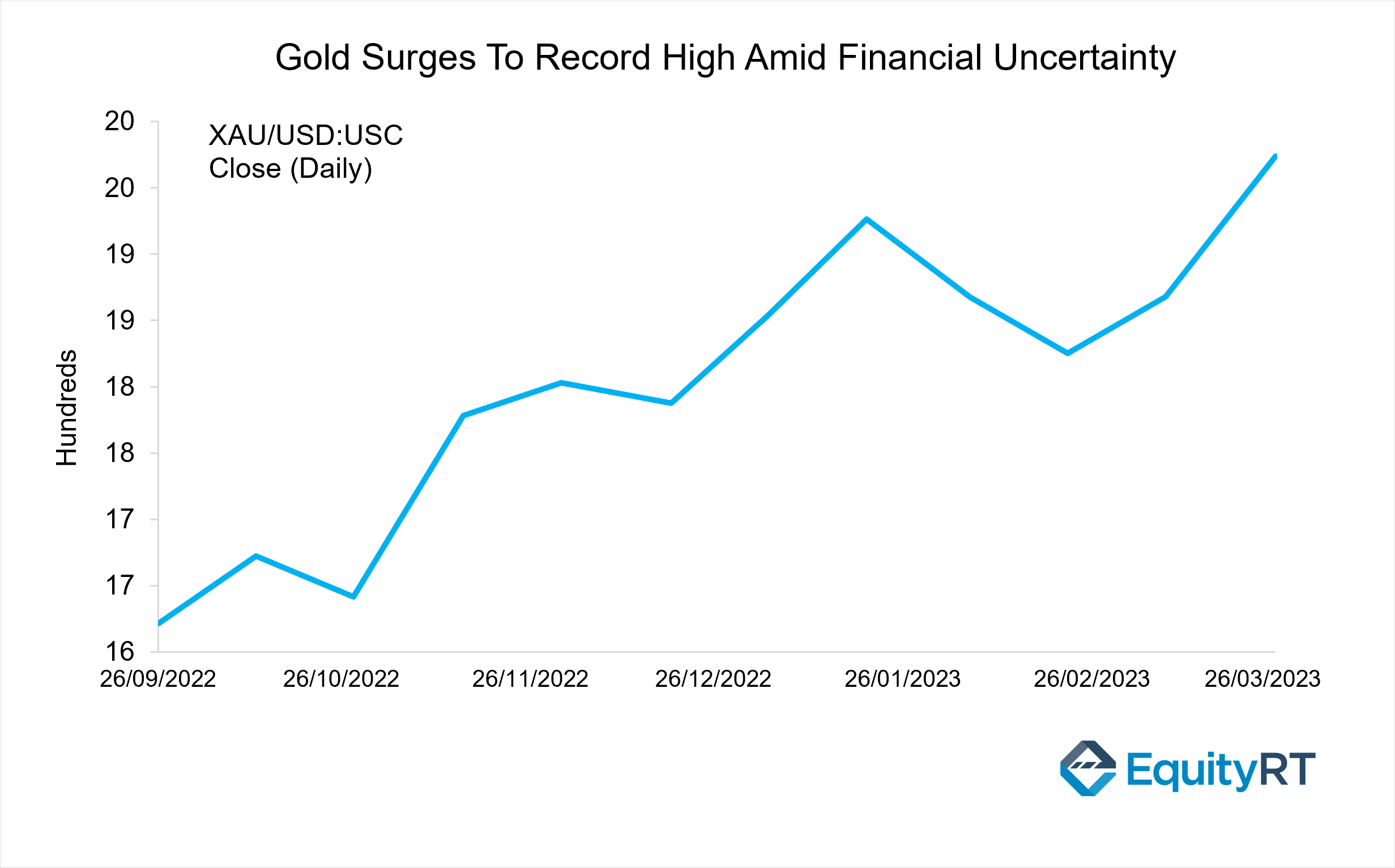
The recent surge in gold prices serves as a reminder of the importance of monitoring the financial health of banks where investments are made.
How can EquityRT help you make informed decisions?
EquityRT is a powerful financial analysis tool that helps investors make informed decisions about their investments. In addition to analyzing the financials of individual stocks, EquityRT also enables investors to track the economic and financial indicators of countries in which they have invested, providing a comprehensive view of their portfolio. This can be particularly useful for investors with international investments, as it allows them to stay informed about global market trends and make more strategic investment decisions.
Overall, EquityRT is a valuable resource for investors looking to maximize the performance of their portfolios.
About EquityRT
Portfolio managers, equity research analysts, economists, and many other investment professionals are constantly challenged to deliver quality research to guide the right investment decisions. Making the right decisions starts with having an optimum investment strategy in place.
