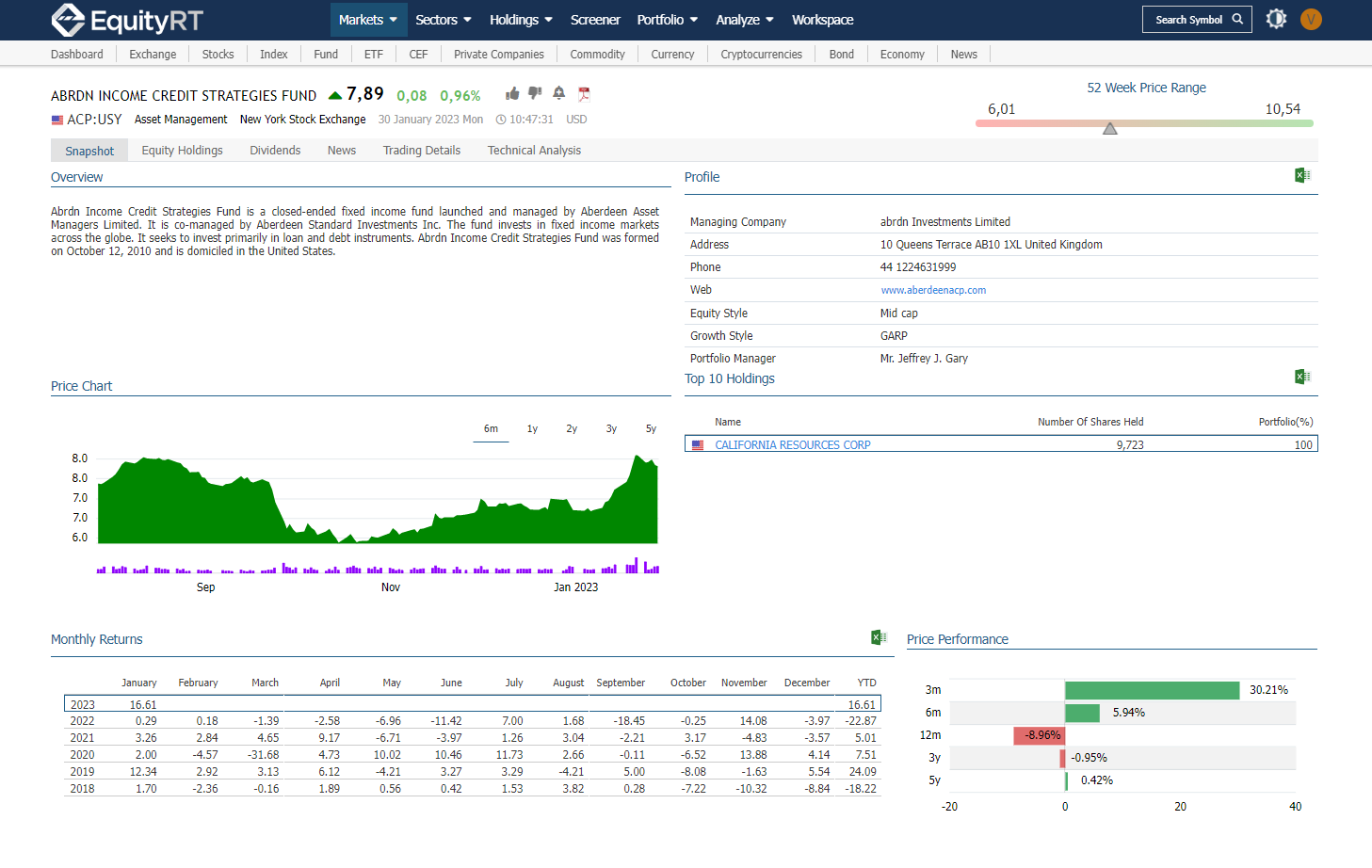
Closed-End Funds
What is a Closed-end Fund?
A closed-end fund (CEF) is a portfolio of pooled assets that raises a fixed amount of capital through an initial public offering (IPO) and then lists shares for trade on a stock exchange. Like a mutual fund, a closed-end fund has a professional manager overseeing the portfolio and actively buying and selling holding assets. Similar to an exchange-traded fund, it trades like equity, as its price fluctuates throughout the trading day. However, the closed-end fund is unique in that, after its IPO, the fund’s parent company issues no additional shares. Nor will the fund itself redeem—buy back—shares. Instead, like individual stock shares, the fund can only be bought or sold on the secondary market by investors.
Shared characteristics of CEFs and traditional mutual funds
- Both have an underlying portfolio of investments with a net asset value
- Both are run by a professional management team
- Both have expense ratios and, typically, fee schedules
- Both may offer distributions of income and capital gains to investors
Shared characteristics of CEFs and ETFs
- Both have an underlying portfolio of investments with a net asset value
- Both trade during the day on exchanges
- Both can be treated very much like a stock, in that you can set limit orders, short the shares, and buy on margin
- Both have expense ratios and, typically, fee schedules
- Both may offer distributions of income and capital gains to investors